Docker for Beginners: Getting Started Step-by-Step


Installation of Docker
Mac and Windows Installation
For mac and windows the easiest way to getting started with docker is to install Docker desktop from their official site. You can find the installation link below.
Link to Download ---> Docker Desktop
Just download the application and install on you machine.
Linux Installation
For debian based distro like ubuntu simply use snap package to install and remove docker
sudo snap install dockercmakeNow check if it is installed correctly by running
docker --versionadaAdditionally we can add our user to docker group, so that we don't have to prefix our docker command with sudo everytime.
To add user to the docker group simply run this command (For linux only)
useradd -aG docker <you-user-name>pgsqlGetting started with Docker
Now docker is installed in our system, we will verify by running the first container.
docker run hello-worldrouteros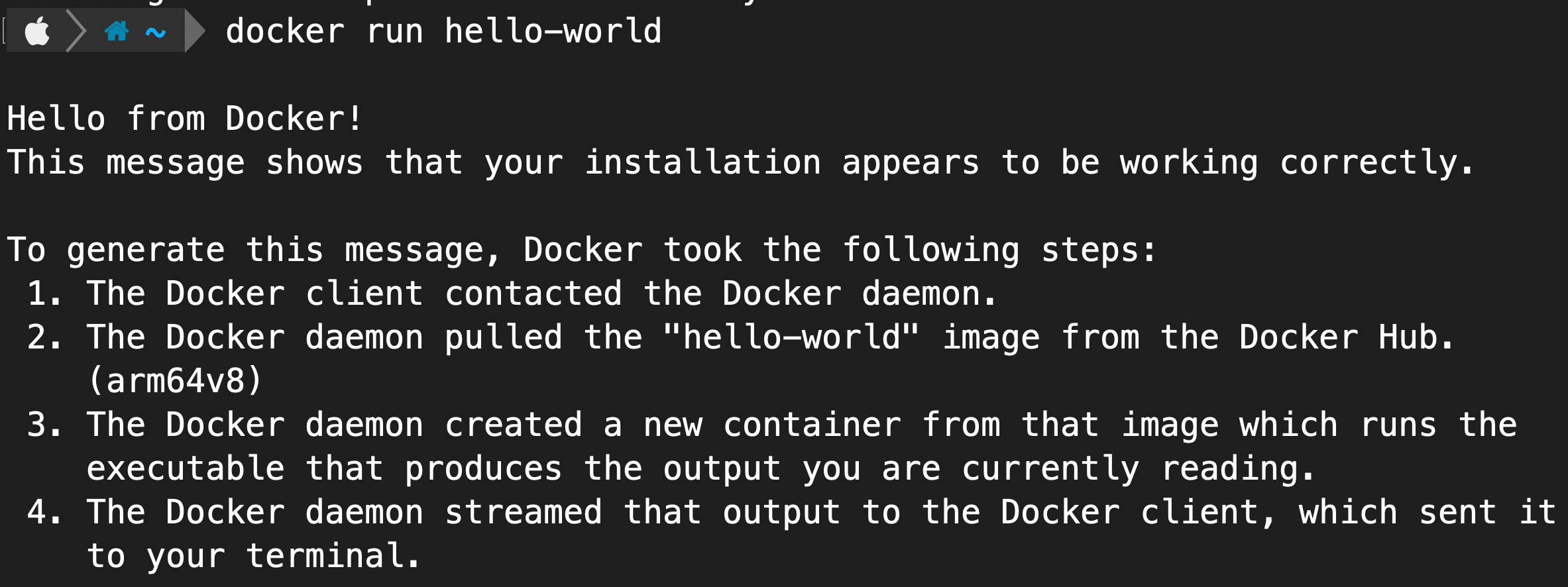
What is a Docker Container?
A Docker container is an isolated environment on a host machine used to run applications and services. Containers are similar to virtual machines, but they do not have their own operating system. Instead, they share the host OS kernel. Each container has its own file system, process tree, and network configuration, making it lightweight and efficient.
Why Is Docker Required?
Every application requires specific dependencies and packages to run. Problems arise when multiple applications need the same dependency but different versions, or when an application needs to scale quickly under increased load.
Initially, Virtual Machines (VMs) were used to solve this by creating multiple environments on a single host. While effective, VMs are resource-intensive because each VM requires its own operating system, making them harder to manage and expensive to scale.
Containers, like Docker, solved this problem by sharing the host OS, making them lightweight, fast, and portable. Docker containers can run consistently across different environments, from local machines to cloud servers.
What Can You Run on Docker?
Anything that runs as a process can be containerized using Docker. This includes:
Web applications written in Python, Java, .NET, Node.js, etc.
Databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL
Background services, APIs, and even games 😄
How Does Docker Work?
Docker uses the concept of images. A Docker image is a blueprint that contains everything needed to run an application—code, dependencies, and configurations.
You can create multiple containers from the same image, which makes scaling applications easy.
To run a container from an image, use:
docker run <image-name>
For example:
docker run hello-world
Here,hello-worldebnfWhat’s Next?
To learn more about Docker, check out my upcoming blog: Docker for Developers (Coming Soon 🚀)
Thanks for reading!